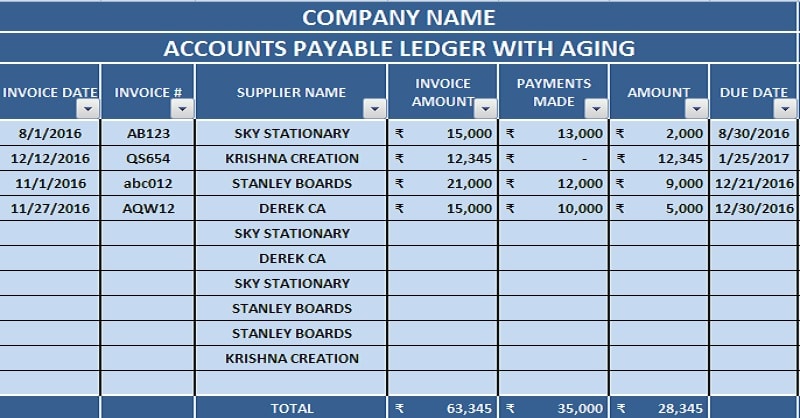
How to Calculate Accounts Payable: A Guide to AP Formula
The outstanding payment owed to suppliers and vendors by a business will remain constant until the payment obligation is fulfilled (i.e. the payment is paid for in-full via cash). Said differently, the accounts payable of a company (or buyer) is the accounts receivable of the 3rd party supplier or vendor owed money for goods and services already delivered. This metric helps gauge the efficiency of your AP management by analyzing your total purchases against your accounts payable.

Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio illustration
Accounts payable automation offers finance teams greater operational flexibility by streamlining and simplifying their processes. Moreover, features like real-time reporting and analytics allow finance teams to quickly adapt to changing business needs and make more informed decisions, enhancing their agility and responsiveness. If you wait too long to pay, you may damage your relationship with the vendor. Reliable vendors are important, and you need to pay them in a timely manner. The vast amount of your payables should be in the 0-to-30-days-old category. Since most invoices are due within 30 days, you don’t want many outstanding invoices unpaid beyond 30 days.
What are the Core Tasks of the Accounts Payable (AP) Department
If a company purchases goods, the bill helps trace the quantity of what was received. AP is also a direct line of contact between a business and its vendor representatives. Strong business relationships between the two could benefit the company and a vendor might offer relaxed credit terms. As a result, there will be no need for you to manually enter or upload all your invoices, and your purchase and payment process would also get automated.
Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
Ensure that the bill includes vendor name, authorization, date, and verified and matching requirements to the purchase order. You’ll also need to include certain clauses in the supplier contract relating to penalizing suppliers, this is in case of non-performance or underperformance. Your DPO doesn’t just tell you about your own business; it also tells you how you stack up against others in your field. If your DPO is much higher than average, it could mean you’re out-negotiating competitors or it could warn of potential cash issues. The term “payable”, in the context of Accounts Payable, means expected to be paid.
Understanding the dynamics of Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable
The current ratio will change slightly depending on the amount of the current assets and the current liabilities. If accounts receivable is the next best thing to cash for a company, then accounts payable is the next worst thing as it is bills waiting to be paid. Understanding how to calculate accounts payable is important to the success of any business. Relying on an incorrect accounts payable balance can lead to poor business decisions, and damage relationships with vendors.
Will my accounting software calculate accounts payable?
The debit could also be to an asset account if the item purchased was a capitalizable asset. When the bill is paid, the accountant debits accounts payable to decrease the liability balance. The offsetting credit is made to the cash account, which also decreases the cash balance. The payable is essentially a short-term IOU from one business to another business or entity. The other party would record the transaction as an increase to its accounts receivable in the same amount.
- This could result in a lower growth rate and lower earnings for the company in the long term.
- It’s a great tool to help you identify potential omissions within the AP workflow so that you can improve and optimize invoice processing.
- The owner should review all of the documents before signing the check and paying the invoice.
- For example, the ‘Accounts Payable Aging Summary’ report, not only tells you about the vendors that you owe money to, but it also highlights the invoices against which payments are overdue.
- During the month, your company purchased $5,000 worth of goods and services on credit, and made $7,500 in payments to suppliers.
If these balances don’t match, you will need to review the subledger to identify any errors. Accounts payable is the amount of money you owe suppliers, vendors, employees, and other third-party individuals or companies for providing a product or service to you. In other words, accounts payable is credit extended to you by a third party allowing you to pay sometime in the future. Manual accounts payable processes waste time and money, and often cause costly errors. Read on to learn how businesses can improve their accounts payable workflow and help their bottom line.
If your business is smaller, a bookkeeping employee may handle accounts payable. Failure to manage Accounts Payable efficiently can lead to strained supplier relationships, potential supply disruptions, and could negatively impact a company’s cash flow. The accounts payable is listed on the balance sheet under current liabilities. In some companies, one specific accountant may be responsible for all accounts payable.
Automated systems often have built-in security features that help protect financial data. Additionally, they can assist in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of fines and legal issues. To work productively, you need to design an efficient system to manage the payment process. In addition, before making an investment decision, the investor should review other financial ratios as well to get a more comprehensive picture of the company’s financial health. That, in turn, may motivate them to look more closely at whether Company B has been managing its cash flow as effectively as possible. You can set up a list of favored suppliers, this can promote moderate and favorable buying from your suppliers.
This figure reflects all outstanding obligations that the company is yet to settle with its creditors. Accounts Payable (AP) is a current liability representing money owed to customers. Analysing the AP turnover (how long does the organisation take to pay the creditors) regularly can help organisations meet deadlines and avoid delinquencies. Accounts Payable influences a company’s financial performance, credit understanding cash flow statement vs income statement conditions, and capacity to recruit investors and provides essential information about its general financial health. When deciding whether to invest or lend money, investors and lenders use these measurements to evaluate a company’s solvency and management consulting procedures. In this article, we discuss how to calculate accounts payable, what to interpret and conclude from it, and the limits it has.
Based on the increase or decrease tracked on the cash flow statement (CFS), the change in accounts payable is the net impact that impacts the carrying value of the current liability on the balance sheet. In effect, the accounts payable balance increases when a supplier or vendor extends credit, and vice versa when the company pays in cash (and fulfills the payment obligation to its creditors). The accounts payable line item is recorded in the current liabilities section of the balance sheet since the company is expected to pay off the owed supplier payment soon, most often within 30 to 90 days. Incorporating Medius AP Automation into your financial operations can significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of forecasting accounts payable. Medius streamlines this process with cloud automation, ensuring timely and precise calculations essential for strategic decision-making.
